
Table of Contents
引子
K8s 作为一个核弹级的容器编排工具,现在可以说是非常的火
然后好多人不懂如何搭建
今天我就给大家介绍一下
准备说明
- 系统:centos7
- 架构:amd
- 配置:2C2G36G
开始安装
环境准备
# 允许内核做 ip 转发
临时修改
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/bridge/bridge-nf-call-iptables
永久修改
vim /etc/sysctl.conf
#末尾添加
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
sysctl -p 使配置文件生效 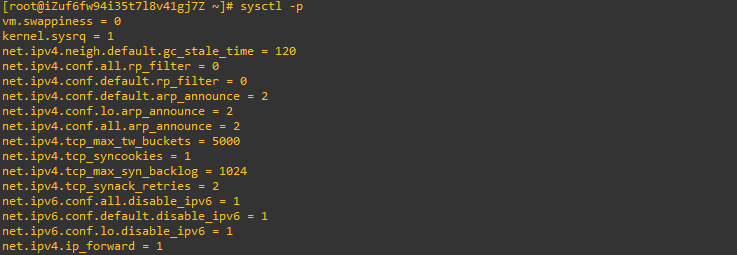
配置 yum 源
本次使用国内阿里云的 yum 源
在 shell 界面输入:
cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
repo_gpgcheck=0
gpgkey=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
EOF
setenforce 0
swapoff -a
yum install -y --nogpgcheck kubelet-1.23.5-0 kubeadm-1.23.5-0 kubectl-1.23.5-0
systemctl enable kubelet && systemctl start kubelet执行结束即安装成功
安装 docker 并启动
yum -y install docker
systemctl enable --now docker之后需要配置一个初始化文件, 注意下面代码中 139 开头的 ip 换成你自己当前服务器的 ip 地址 :
cat <<-EOF >kubeadm_init.yaml
apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta3
kind: ClusterConfiguration
kubernetesVersion: v1.23.5
apiServer:
certSANs:
- "139.196.109.101"
controlPlaneEndpoint: "139.196.109.101:6443"
networking:
podSubnet: 10.244.0.0/16
imageRepository: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers
EOF执行下面的代码开始安装
kubeadm init --config=./kubeadm_init.yaml下面是安装日志,这个安装日志和上面安装初始化的文件都很重要,建议大家保留
# 安装日志如下
[root@iZuf6fw94i35t7l8v41gj7Z ~]# kubeadm init --config=./kubeadm_init.yaml
[init] Using Kubernetes version: v1.23.5
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[preflight] Pulling images required for setting up a Kubernetes cluster
[preflight] This might take a minute or two, depending on the speed of your internet connection
[preflight] You can also perform this action in beforehand using 'kubeadm config images pull'
[certs] Using certificateDir folder "/etc/kubernetes/pki"
[certs] Generating "ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver" certificate and key
[certs] apiserver serving cert is signed for DNS names [izuf6fw94i35t7l8v41gj7z kubernetes kubernetes.default kubernetes.default.svc kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local] and IPs [10.96.0.1 172.16.1.182 139.196.109.101]
[certs] Generating "apiserver-kubelet-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/server" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/server serving cert is signed for DNS names [izuf6fw94i35t7l8v41gj7z localhost] and IPs [172.16.1.182 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/peer" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/peer serving cert is signed for DNS names [izuf6fw94i35t7l8v41gj7z localhost] and IPs [172.16.1.182 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/healthcheck-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver-etcd-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "sa" key and public key
[kubeconfig] Using kubeconfig folder "/etc/kubernetes"
[kubeconfig] Writing "admin.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "kubelet.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "controller-manager.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "scheduler.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[kubelet-start] Starting the kubelet
[control-plane] Using manifest folder "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-apiserver"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-controller-manager"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-scheduler"
[etcd] Creating static Pod manifest for local etcd in "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[wait-control-plane] Waiting for the kubelet to boot up the control plane as static Pods from directory "/etc/kubernetes/manifests". This can take up to 4m0s
[apiclient] All control plane components are healthy after 9.509442 seconds
[upload-config] Storing the configuration used in ConfigMap "kubeadm-config" in the "kube-system" Namespace
[kubelet] Creating a ConfigMap "kubelet-config-1.23" in namespace kube-system with the configuration for the kubelets in the cluster
NOTE: The "kubelet-config-1.23" naming of the kubelet ConfigMap is deprecated. Once the UnversionedKubeletConfigMap feature gate graduates to Beta the default name will become just "kubelet-config". Kubeadm upgrade will handle this transition transparently.
[upload-certs] Skipping phase. Please see --upload-certs
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node izuf6fw94i35t7l8v41gj7z as control-plane by adding the labels: [node-role.kubernetes.io/master(deprecated) node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane node.kubernetes.io/exclude-from-external-load-balancers]
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node izuf6fw94i35t7l8v41gj7z as control-plane by adding the taints [node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule]
[bootstrap-token] Using token: u4by32.6lf1lz7let0wcpuq
[bootstrap-token] Configuring bootstrap tokens, cluster-info ConfigMap, RBAC Roles
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to get nodes
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to post CSRs in order for nodes to get long term certificate credentials
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow the csrapprover controller automatically approve CSRs from a Node Bootstrap Token
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow certificate rotation for all node client certificates in the cluster
[bootstrap-token] Creating the "cluster-info" ConfigMap in the "kube-public" namespace
[kubelet-finalize] Updating "/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf" to point to a rotatable kubelet client certificate and key
[addons] Applied essential addon: CoreDNS
[addons] Applied essential addon: kube-proxy
Your Kubernetes control-plane has initialized successfully!
To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Alternatively, if you are the root user, you can run:
export KUBECONFIG=/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster.
Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/
You can now join any number of control-plane nodes by copying certificate authorities
and service account keys on each node and then running the following as root:
kubeadm join 139.196.109.101:6443 --token u4by32.6lf1lz7let0wcpuq \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:b0fa3c1f3e1905cfd2ce9dc2c7fbcd35e70805e12b30a64818890edd4c5238c8 \
--control-plane
Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root:
kubeadm join 139.196.109.101:6443 --token u4by32.6lf1lz7let0wcpuq \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:b0fa3c1f3e1905cfd2ce9dc2c7fbcd35e70805e12b30a64818890edd4c5238c8
日志解析
日志中的说明了我们如果是普通用户执行:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/configroot 用户执行:
export KUBECONFIG=/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf如果是集群的话,加入一个 master 节点需要执行:
kubeadm join 139.196.109.101:6443 --token u4by32.6lf1lz7let0wcpuq \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:b0fa3c1f3e1905cfd2ce9dc2c7fbcd35e70805e12b30a64818890edd4c5238c8 \
--control-plane而加入 node 节点则执行
kubeadm join 139.196.109.101:6443 --token u4by32.6lf1lz7let0wcpuq \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:b0fa3c1f3e1905cfd2ce9dc2c7fbcd35e70805e12b30a64818890edd4c5238c8网络插件安装
此时,如果我们执行代码 kubectl get nodes
会显示我们的节点状态时 notready 的
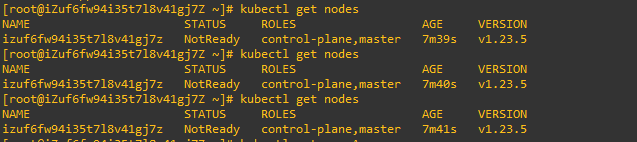
这是因为我们的集群需要安装一个网络插件
这里选用的是 flannel
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/flannel-io/flannel/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml等待大概 2 - 3 分钟即可安装成功
这里我们再次执行 kubectl get nodes 的时候,我们的环境就安装完成了,状态显示 ready

至此,我们的 k8s 一个 master 节点安装完成。
教程编写不易,请大家转载时标注原作
正文完